Write Us
We are just a call away
[ LET’S TALK AI ]
X
Discover AI-
Powered Solutions
Get ready to explore cutting-edge AI technologies that can transform your workflow!

Spatial computing merges the physical and digital worlds!
Spatial computing is a newly emerging technological trend that bridges the physical and digital realities of the present-day world characterized by swift advances in the digital environment. Therefore, entrepreneurship changes enterprises’ relations with technology and opens new horizons and avenues. It aims to improve efficiency and communication, reinvent customer experiences, and reshape various businesses with leading-edge technologies.
The spatial computing market demonstrates rapid expansion which analysts predict through 2022 to 2032. The 3G and 4G network spending by governments worldwide is predicted to reach $2.72 trillion in 2016-2026 while Future Market Insights anticipates the market to grow at an 18.2% compound annual growth rate during 2017-2022. The market demonstrates exponential expansion because industries recognize their growing need for spatial computing solutions which indicate how modern technology transforms sectors and industries.
This blog examines spatial computing as well as its practical uses as well as business implications. Organizations can apply this cutting-edge technology to generate new solutions and seize market possibilities and defeat competitors within the evolving digital sphere.
Start with us and learn more about Spatial Computing.

Spatial computing is a new technological platform that augments digital technology with physical ones to enable the interaction of humans, machines, and spaces. Initially defined by Simon Greenwold, a student at the MIT Media Lab, in 2003, the term describes a world where technology employs physical space as a surface. Today, using the technologies of extended reality (XR), which embraces virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), this idea looks quite realistic.
Spatial computing uses space to communicate or, freeing machines to exist in space, incorporates them into the space continuum. According to Gartner, virtual reality presents pools of realistic digital and computer-aided 3D worlds in which the end-user can interact naturally. Augmented reality (AR) adds digital information, including but not limited to texts, graphics, sounds, and images on real-world objects in real time. With VR, the application is immersive, while with AR, it is context-based, making the whole spatial computing process the integration of digital objects into our natural environment.
Such an integration of cyberspace and the actual environment gives rise to live interfaces that enable users to drive, manage, and operate data and content within actual environments. Spatial computing holds great potential for manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and education industries with iOS app development company. By altering how humans can process and interface with data, spatial computing is building a world in which technology exists and fades in as a part of society.
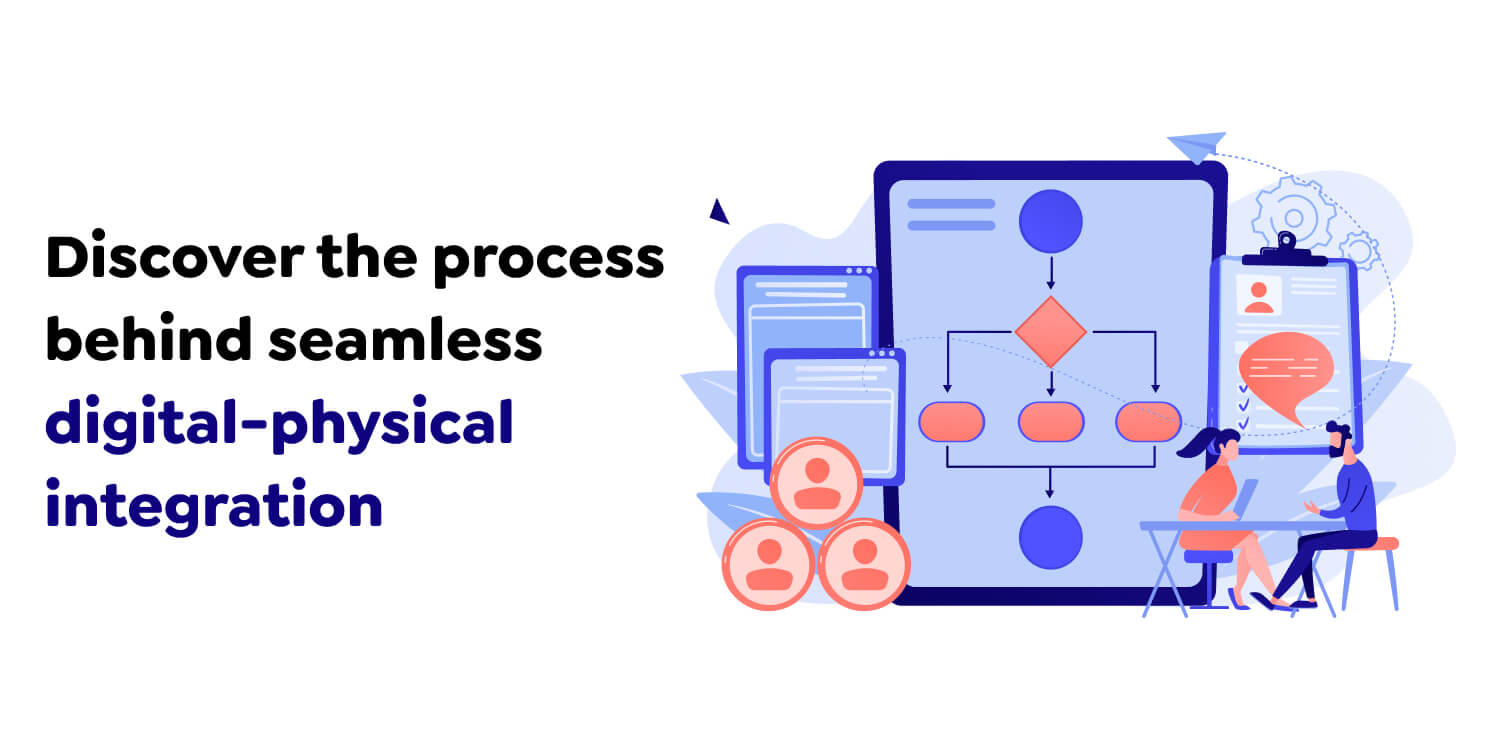
Spatial computing goes through key processes that enable it to convert the raw spatial data from the physical environment into enhanced information and accessible interactions. It develops models of fundamental physical environments for interaction and decision-making strategies using intensive sensors, mathematical algorithms, and visualization techniques. The key stages in spatial computing include in process of visionOS app development:
It starts with acquiring data in space from a real-world environment through various sensors, including cameras, LiDAR, and GPS. These devices record complete information concerning the shape and size of the deployment area, the position of objects, and their relative positions, which constitute the fundamental understanding apparatus of spatial environments.
After collecting the data, processing begins to refine it to more meaningful information, removing noise, calibrating the sensor inputs, and fusing the data. Thus, uniting the obtained data arrays creates a complete and accurate representation of the environment for further analysis.
The processed data is then delineated into digital avatars of physical space. This stage includes building 2D or 3D representations embellished with data on object sizes, locations, and relative positioning. These maps act as the basic environments for spatial computing applications, with the potential for exact superimposition of the virtual and physical.
In this step, the digital representation of the environment is analyzed to uncover patterns, trends, and insights. Advanced algorithms and tools are used to process this data, supporting tasks such as predicting outcomes, optimizing layouts, or planning interventions. Applications range from urban development and logistics to environmental monitoring and resource management.
The last step is visualizing the analyzed information to be understood and shared with users through various rollers, content, or games. Hence, with maps, dials, or other stereoscopic interfaces involved in ‘spatial computing,’ it is generated that the users can naturally understand the outcomes. This viz work makes decision support, teamwork, and stakeholder involvement possible in various application areas.
By aligning these stages, spatial computing allows businesses to transition naturally from physical to digital environments. A mobile app development company in UK enables organizations to utilize spatial intelligence, optimize their processes, and provide unique solutions for their needs.

Spatial computing combines advanced hardware and software to deliver engaging, immersive digital experiences. Its key features include:
It relies on sensors like cameras, LiDAR, and GPS to capture data from the physical environment, enabling real-time tracking of position, movement, and environmental variables.
Processes and interprets visual data, enabling systems to recognize objects and people for enhanced interactive experiences.
It uses AI to analyze data, improve sensor accuracy, detect patterns, and provide predictive insights, allowing systems to adapt and optimize over time.
Integrates digital information seamlessly into the physical world to create interactive and enriched real-world experiences.
Develops fully digital, immersive environments that simulate real-world user interaction and engagement scenarios.
Develop abstracted digital renderings of actual space that encode given layouts and positions of objects for context-aware and fully embodied interaction.
Each of these features, working in unison, allows spatial computing to become the bridge between the physical and digital worlds, changing how we engage with technology.
Also Read : Which AR/VR Testing Tools Are Best For Your App?

Spatial computing offers numerous advantages to enterprises, transforming how they operate and interact with technology. Here are some key benefits:
Using spatial computing, teams can experience defined environments best represented in 3D. They can also do virtual simulations of various items or data sets, analyze the data in the defined environment, and make proper decisions. For instance, architects can harness spatial computing to produce animated 3D models, enabling clients to view the building designs and concepts with specific and clear visions rather than relying on real-life models with mere abstract ideas during construction.
Spatial computing also offers a realistic experience whereby training simulation is more accurate and interactive. Especially in sectors like healthcare and aerospace, workers can simulate operations where mistakes could cost them lives – and become more effective and confident in the process. For example, physicians can use actual reality to try operation procedures in operations, enhancing their accuracy.
Spatial computing improves remote assistance and interaction by providing real-time assistance through Augmented Reality (AR) or Mixed Reality (MR) devices. Independent professionals can help field technicians in the actual work execution process, saving time and avoiding unnecessary interaction. This is particularly relevant for vast and complex industries, such as telecommunication and energy industries.
Spatial computing is customer-engaging because it provides tangible responses to inquiries. In retailing, AR can give customers a feel for certain products, such as clothes, through virtual trials or simulations of how a particular piece of furniture will look in their homes. This improves people’s interest and customer satisfaction.
Visual representation and information analysis are transformed through spatial computing, available in three dimensions. Enterprises can analyze datasets in a more appealing way that is far simpler to comprehend. For example, professionals like data analysts and researchers are visually informed by molecular models, which has improved research and quicker drug development.
Integrating the real world with digital content that spatial computing offers means new avenues for enterprises to innovate, facilitate communication, and provide better customer experience.

Spatial computing has found practical use across various industries, transforming operations and enhancing user experiences. Here are some notable examples:
Virtual reality and augmented reality are critical to enhancing the quality of patient care in the context of spatial computing. For example, researchers from the University of Alberta have created ProjectDR, which applies spatial computing and projects the scans as CT on the patient’s physical body in real space and interactive mode.
In retail, IKEA Place is incredibly significant to shopping as it employs augmented reality (AR). This application allows the customer to ‘try’ placing furniture and home decor ordered from IKEA in the comfort of their house, hence making the right decisions.
One example is Microsoft’s HoloLens, which revolutionized construction and architecture by letting professionals project 3D models into the real world. This technology facilitates planning, coordination, and problem-solving during construction.
An example of spatial computing is Ford’s use of gravity Sketch to design automotive parts and develop complex 3D models. This helps designers not work with everyday 2D sketches, which may be time-consuming, but with more natural and informative environments.
Spatial computing is also becoming popular in corporate training, especially in energy industries. Computer-generated 3D environments allow employees to engage in realistic and immersive learning experiences, replicating real workplace scenarios for better skill development.
GE is a prime example of spatial computing’s impact on the enterprise. Technicians equipped with AR glasses experienced a 34% productivity boost. These AR tools provide immersive access to critical information during tasks, significantly improving efficiency and performance.
These real-world examples demonstrate how spatial computing transforms industries, drives innovation, and enhances productivity and user engagement.
Also Read : How Augmented Reality Apps Are Transforming The Learning Experiences?

Implementing spatial computing in enterprises comes with its fair share of challenges. Addressing these hurdles is crucial for the successful adoption and integration of spatial computing technologies. While spatial computing offers numerous benefits, enterprises must navigate these obstacles carefully:
Integrating spatial computing technologies can be expensive, particularly for smaller businesses or those with limited budgets. Costs associated with hardware, software, and training can be significant, creating entry barriers for many enterprises.
Spatial computing often involves collecting sensitive data from physical environments and users. Data privacy and security are critical to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of this information.
Enterprises typically have established systems and workflows in place. Integrating spatial computing seamlessly with existing infrastructure requires careful planning to avoid disruptions to current operations.
Many spatial computing applications rely on stable internet connectivity and high bandwidth. In areas with limited infrastructure, this can hinder the smooth operation of spatial computing solutions.
Adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards adds complexity to implementing spatial computing. Enterprises must ensure compliance with local and global regulations, which vary depending on their location and industry.
These challenges highlight the need for strategic planning and resources to adopt spatial computing in enterprises and maximise its transformative potential.
Also Read : Into the Metaverse: Pioneering the Next Frontier in App Development

The future of spatial computing and digital transformation holds immense potential for driving innovation in enterprises. As technology evolves, spatial computing will enable businesses to experience a significant shift.
This approach will transform operations, enhance productivity, and enable seamless collaboration through real-time access to data. Decision-making and problem-solving processes will benefit from faster insights, and spatial computing will provide immediate information.
Additionally, employees will engage in immersive training experiences, allowing hands-on simulations and skill development. Data visualization and analytics will reach new heights, delivering deeper insights that support informed decision-making across various industries.

Techugo, a leading AR/VR development company, is your ideal partner in unlocking the full potential of augmented and virtual reality for your business. With our deep expertise, we create highly immersive experiences that engage users and deliver exceptional results. Here’s how we can support you:
Our team specializes in designing cutting-edge AR and VR solutions. We take users into captivating virtual environments, boosting engagement and leaving a lasting impression.
We work closely with clients to fully understand their unique business needs and goals. Our bespoke AR/VR solutions are crafted to perfectly align with your vision and cater specifically to your target audience.
We leverage the latest tools and technologies to create innovative AR/VR experiences that set your business apart. This ensures you stay ahead of the curve in this rapidly evolving field.
We deliver results quickly and efficiently using an agile, user-centric approach. We value regular feedback and iterative improvements, ensuring that your solutions are constantly refined to perfection.

Spatial computing transforms how modern businesses engage with technology, creating immersive experiences and driving productivity. By seamlessly integrating AR, VR, and MR, this technology bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds. The rapidly growing spatial computing market presents immense opportunities across various industries.
To unlock the full potential of spatial computing, Techugo, with its tailored AR development services, provides innovative solutions and cutting-edge technology for businesses.
Get in touch with Techugo today to explore how we can help you embrace this digital frontier and thrive in a new wave of innovation.
Write Us
sales@techugo.comOr fill this form